
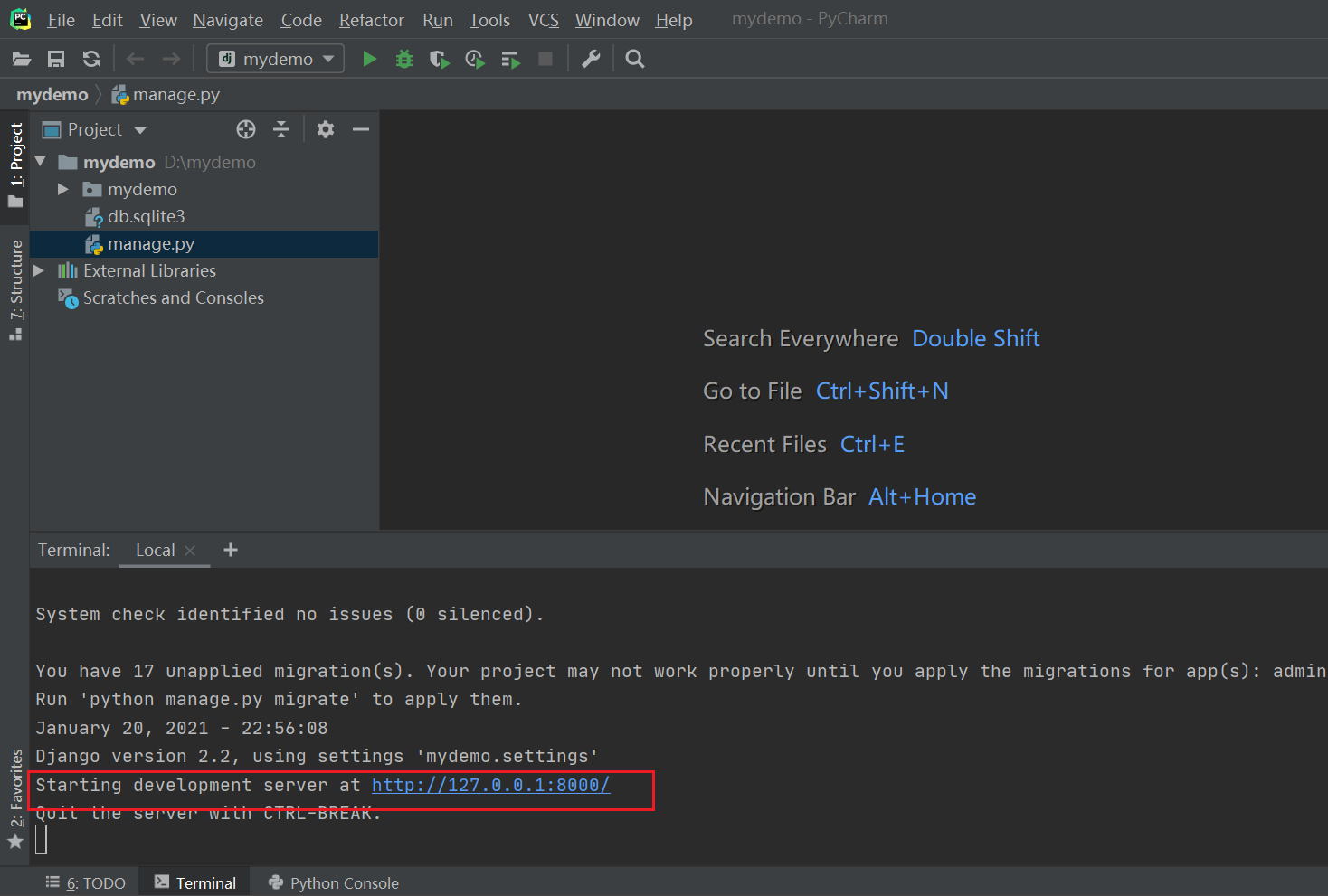
in the upper right.Ĭlick on the plus sign in the upper left part, and select Django Server. Click on Apply and then OK.įinally, you have to configure a Django server. ├── manage.py # this is the Manage scriptįifth, enable the Django support in Preferences -> Languages & Frameworks -> Django.Ĭheck Enable Django Support, and provide the Django project root, Settings, and Manage script.
#RUN DJANGO SERVER IN PYCHARM PROFESSIONAL INSTALL#
P圜harm will automatically recognize the virtual environment that you previously created, so if you open a terminal inside P圜harm, you will see the interpreter is actually set.įourth, from the terminal, install Django using pipenv and create a new project called mysite $ pipenv install djangoĪfter running this commands your project directory should look like this: Browse to mysite directory, and click on Open. Third, open up P圜harm, and click on Open. Second, let's create a virtual environment using pipenv: $ pipenv -three I will call this directory mysite, and I will navigate inside of it. !#! Previous versions of P圜harmįirst, let's create a project that will have the name of our Django project. Click on the play button in upper run corner and you will see the Django launch page you can see at the end of this answer. Wait to P圜harm to create a virtual environment, install Django, and and index files. I strongly recommend using pipenv to manage your packages.
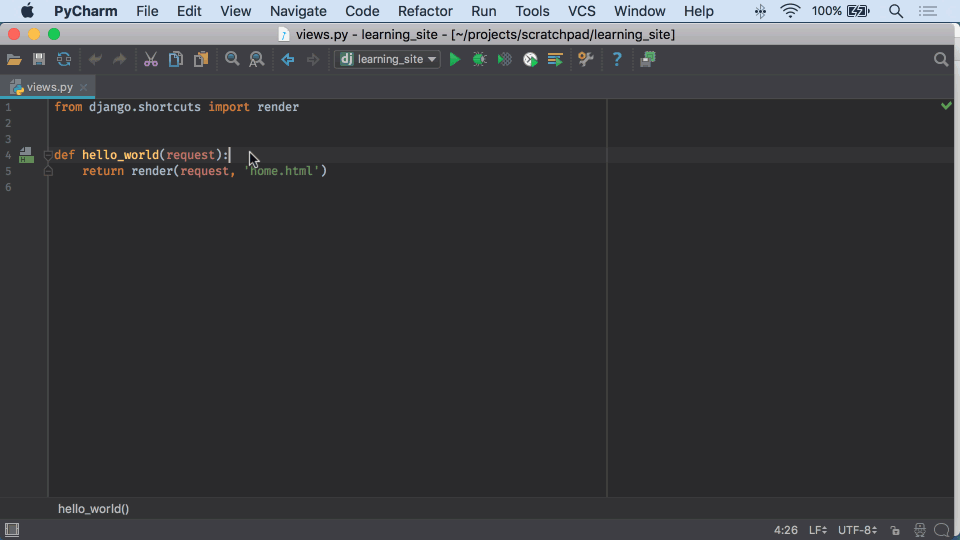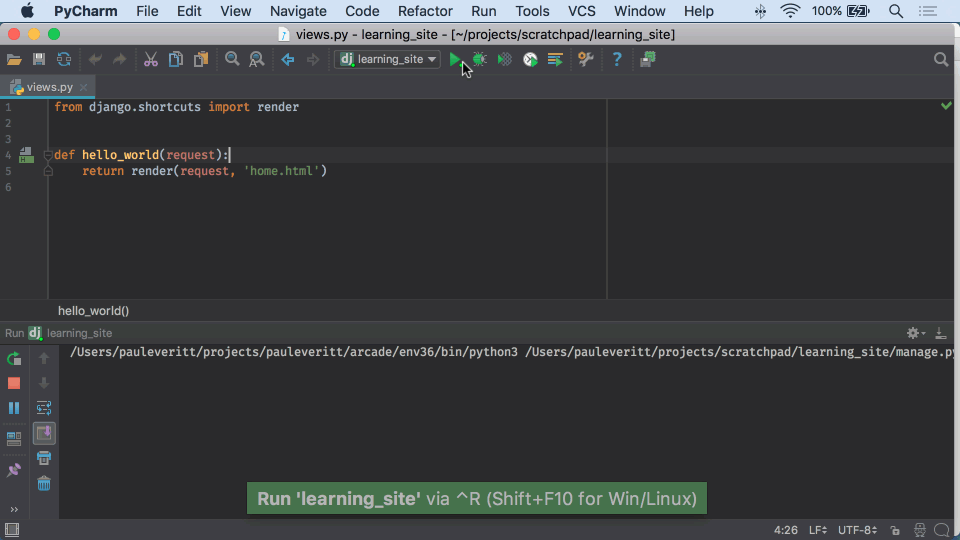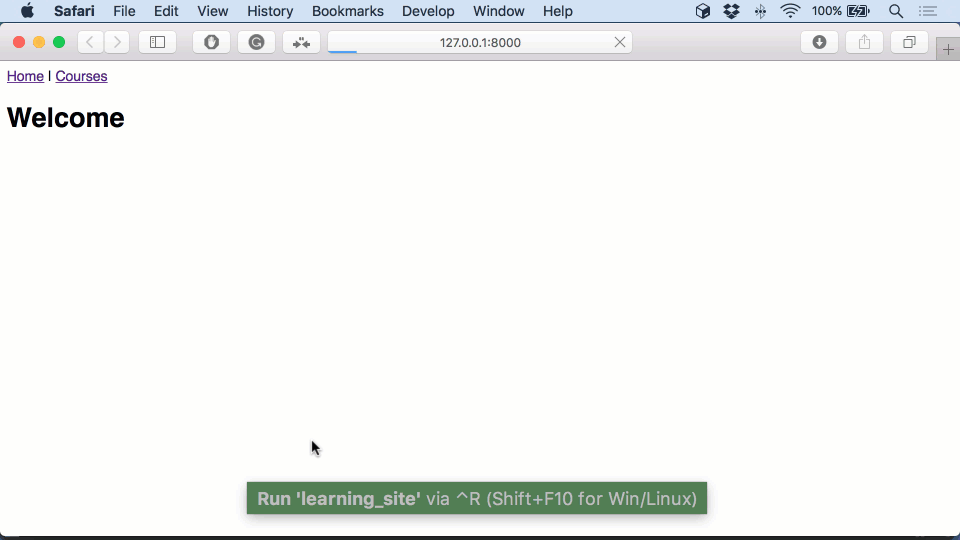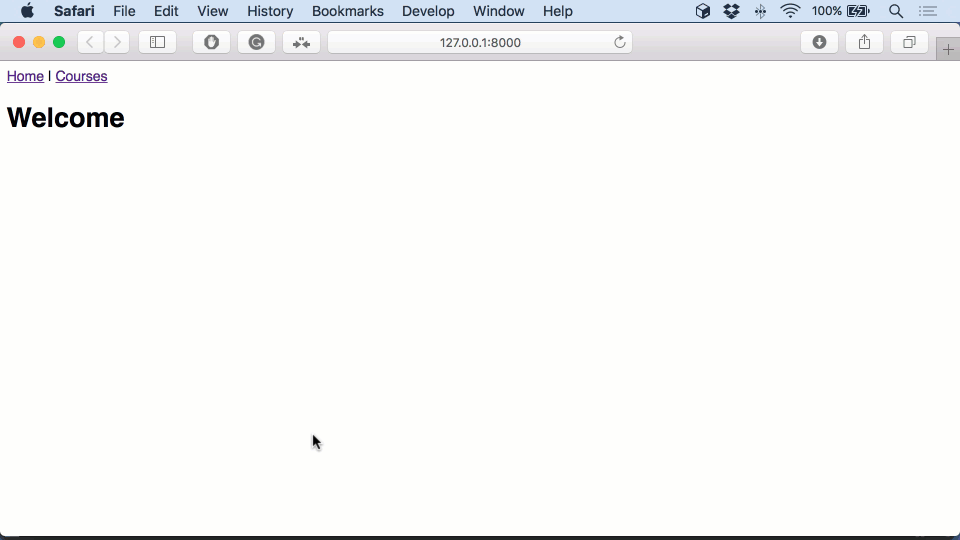
Open P圜harm, and select Create New Project.I can state that it has become pretty simple the way to start a Django project. I use Python 3, so I will also use Django 2. Note: I use pipenv to install dependencies, so I will assume you have it installed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
